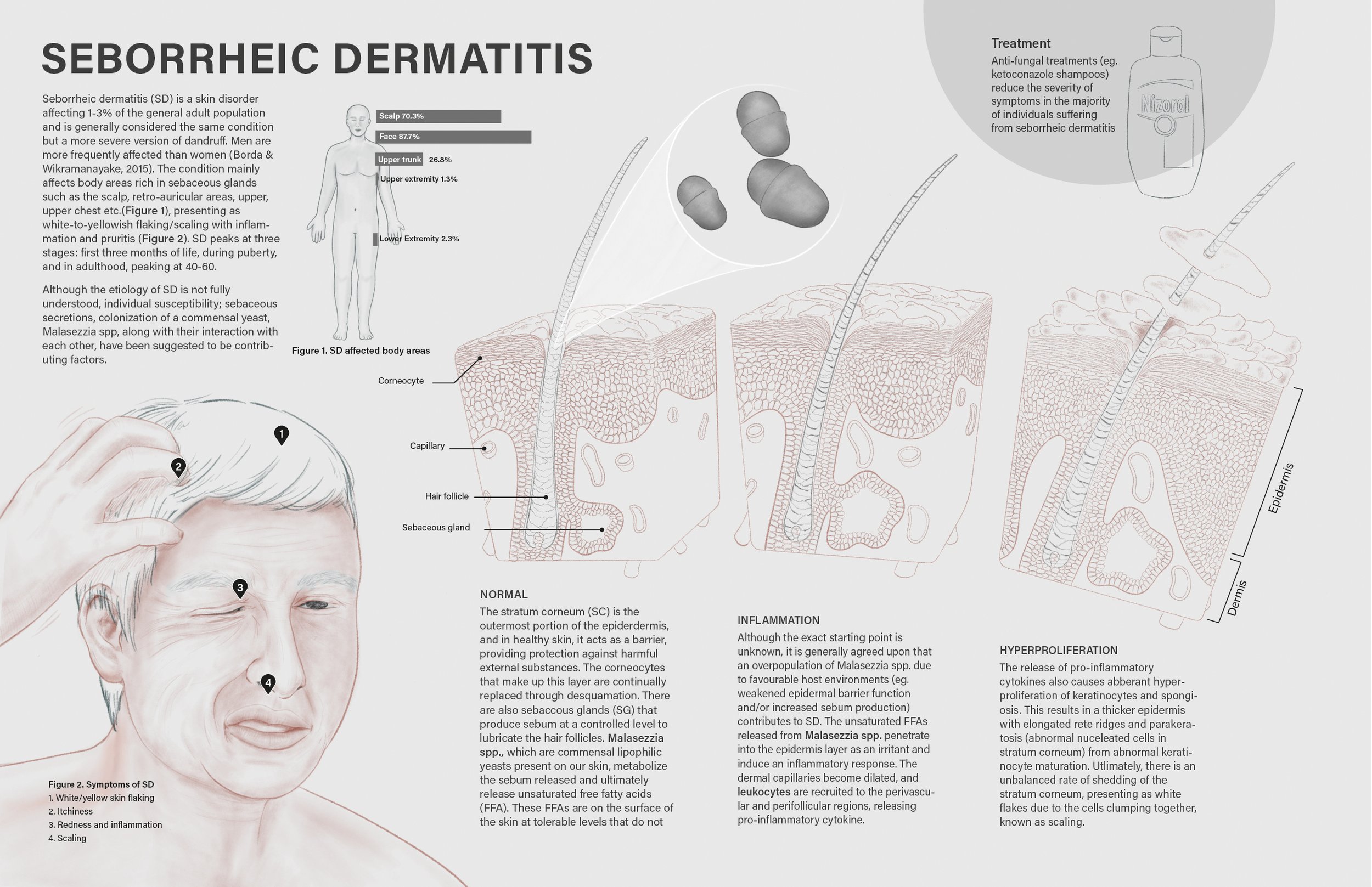
Pathology: Seborrheic Dermatitis
A mock 11x17" science magazine spread depicting the pathological process of seborrheic dermatitis (SD) at the tissue level in addition to the clinical presentation. SD is a skin condition that is considered a more severe version of dandruff, which is associated with the overpopulation of Malessezia spp. yeast on human hosts due to various biological and environmental factors.
Client: Prof. Dave Mazierski & Dr. John Wong
Media: Procreate, Adobe Illustrator
Format: 11X17” magazine spread
Audience: Educated lay audience
Date: December 2021
Process work
Research
I reviewed the literature to understand the clinical presentations of SD, the affected population, the etiology of the condition, and treatments. I also reviewed the tissue-level changes through histological figures to segregate stages of progression. This was used to develop the final text and illustrations for the spread.
Concept + Layout Sketches
I created a maquette of my three tissue cubes in Autodesk Maya as a perspective guide for the sketches and final rendering stage.
Preparatory Study: Colour Thumbnails
Cleaned Line Art
Final
References
Adalsteinsson, J. A., Kaushik, S., Muzumdar, S., Guttman-Yassky, E., & Ungar, J. (2020). An update on the microbiology, immunology and genetics of seborrheic dermatitis. Experimental Dermatology, 29(5), 481–489. https://doi.org/10.1111/EXD.14091
Borda, L. J., & Wikramanayake, T. C. (2015). Seborrheic Dermatitis and Dandruff: A Comprehensive Review. Journal of Clinical and Investigative Dermatology, 3(2). https://doi.org/10.13188/2373-1044.1000019
Krstic, R. V. (1994). Human Microscopic Anatomy: An Atlas for Students of Medicine and Biology. Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg GmbH.
Pople, J. E., Bhogal, R. K., Moore, A. E., & Jenkins, G. (2019). Changes in epidermal morphology associated with dandruff. International Journal of Cosmetic Science, 41(4), 357–363. https://doi.org/10.1111/ICS.12539
Sampaio, A. L. S. B., Mameri, Â. C. A., Vargas, T. J. de S., Ramos-e-Silva, M., Nunes, A. P., & Carneiro, S. C. da S. (2011). Seborrheic dermatitis. Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia, 86(6), 1061–1074. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0365-05962011000600002
Schwartz, J. R., Messenger, A. G., Tosti, A., Todd, G., Hordinsky, M., Hay, R. J., Wang, X., Zachariae, C., Kerr, M., Henry, J. P., Rust, R. C., & Robinson, M. K. (2013). A Comprehensive Pathophysiology of Dandruff and Seborrheic Dermatitis-Towards a More Precise Definition of Scalp Health. Acta Derm Venereol, 93. https://doi.org/10.2340/00015555-1382
Skin Problems and Treatments: Guide to Seborrheic Dermatitis. (2021, January 14). EMedicineHealth. https://www.emedicinehealth.com/skin_treatments_problems_seborrheic_dermatitis/article_em.htm
Vijaya Chandra, S. H., Srinivas, R., Dawson, T. L. J., & Common, J. E. (2021). Cutaneous Malassezia: Commensal, Pathogen, or Protector? Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 0, 869. https://doi.org/10.3389/FCIMB.2020.614446
Wikramanayake, T. C., Borda, L. J., Miteva, M., & Paus, R. (2019). Seborrheic dermatitis—Looking beyond Malassezia. Experimental Dermatology, 28(9), 991–1001. https://doi.org/10.1111/EXD.14006
William K. Ovalle, P. C. N. (2013). Netter’s Essential Histology (Second). Elsevier Saunders.
123RF. (n.d.). Stock Photo. https://www.123rf.com/photo_19483500_senior-man-scratches-his-itchy-scalp.html